The term “Private Society Kendra” often piques curiosity, conjuring images of exclusive groups operating beyond conventional norms. While the specifics behind “Kendra” remain ambiguous without further context, this exploration delves into the ethical considerations surrounding private societies and their potential impact on individual freedom and social harmony.
The Allure and Concerns of Private Societies
Throughout history, humans have gravitated towards forming communities, seeking belonging and shared ideals. Private societies, with their air of mystery and exclusivity, can hold a certain allure. They often promise access to knowledge, influence, or resources unavailable to the general public. However, this exclusivity also raises ethical red flags.
- Transparency and Accountability: Private societies, by their very nature, often operate with a degree of secrecy. This lack of transparency can mask potential wrongdoing, making it difficult to hold members accountable for their actions.
- Discrimination and Bias: The selection criteria for joining a private society can perpetuate existing social inequalities. If membership hinges on factors like wealth, lineage, or social connections, it can exacerbate social divisions and discrimination.
- Conflicting Loyalties: Being part of a private society can create conflicting loyalties. Members might feel torn between the interests of the society and their responsibilities to the larger community.
- Erosion of Trust: When a society operates under a veil of secrecy, it can breed mistrust and suspicion within the wider community. This erosion of trust can hinder open dialogue and cooperation.
 Private Society Meeting
Private Society Meeting
Balancing Individual Freedom and Collective Responsibility
A fundamental ethical dilemma arises when the pursuit of individual freedom within a private society clashes with the well-being of the larger community. For instance, if a society’s practices promote discrimination or harm others, it infringes upon the basic rights and freedoms of those excluded or targeted.
Dr. Emily Carter, a sociologist specializing in group dynamics, notes, “Private societies can foster a sense of ‘us versus them,’ which can lead to the dehumanization of those outside the group. This can have dangerous consequences, justifying prejudice and even violence.”
Finding a balance between individual freedom and collective responsibility requires open dialogue and a willingness to examine the potential consequences of actions.
The Importance of Ethical Frameworks
To navigate the ethical complexities of private societies, it’s crucial to establish clear ethical guidelines. These frameworks should address issues like:
- Transparency: While maintaining some degree of privacy might be necessary, private societies should be transparent about their core values, mission, and activities that impact the public sphere.
- Inclusivity: Membership criteria should be based on merit and shared values, rather than discriminatory factors.
- Accountability: Mechanisms should be in place to hold members accountable for any ethical violations or harm caused by their actions within the society.
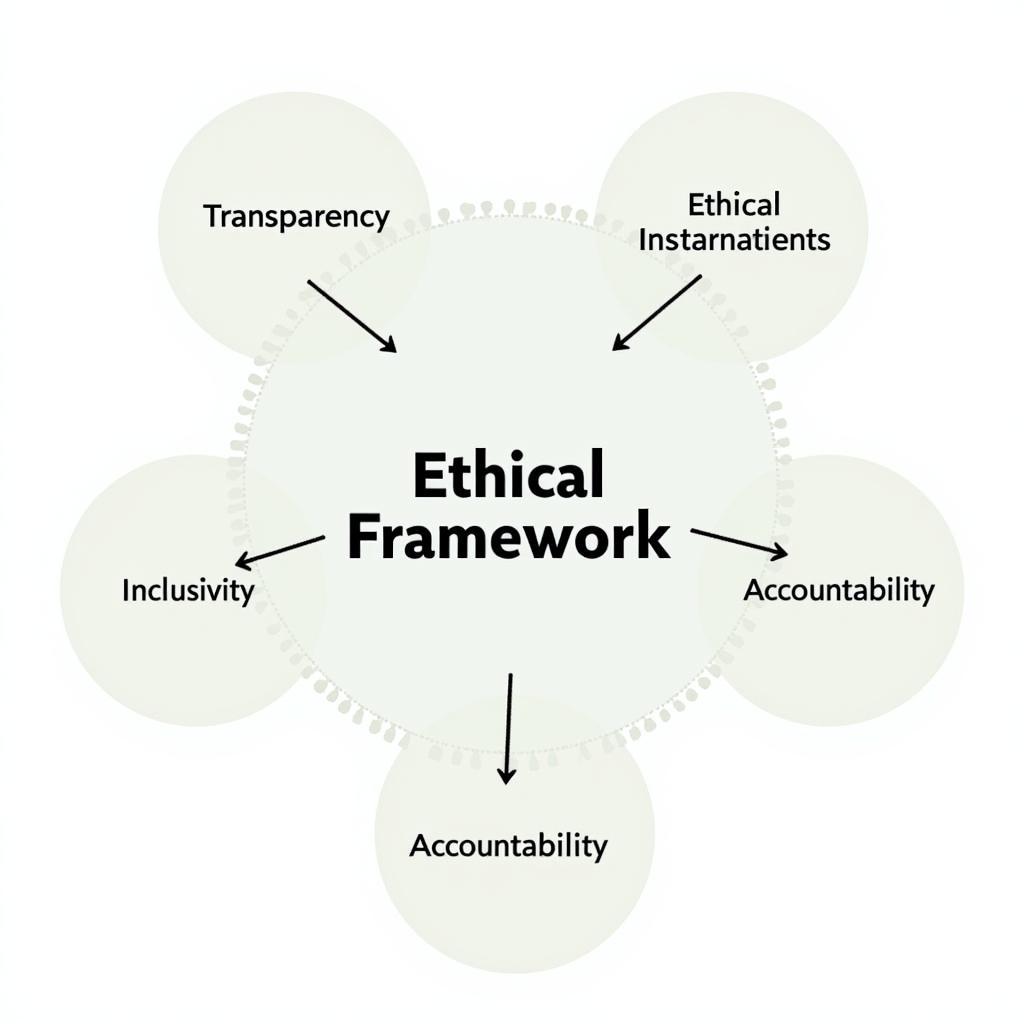 Ethical Framework Diagram
Ethical Framework Diagram
Fostering a More Just and Equitable Society
Ultimately, the ethical implications of private societies depend on their actions and impact on the world. When private societies operate with transparency, inclusivity, and a commitment to the greater good, they can contribute positively to society. However, when they function in secrecy, perpetuate inequality, or prioritize self-interest above all else, they can be detrimental to social harmony and justice.
Dr. James O’Connell, an ethicist specializing in organizational behavior, suggests, “Private societies should engage in critical self-reflection, asking themselves how their actions align with their stated values and whether they contribute to a more just and equitable world.”
Conclusion
“Private society Kendra” serves as a springboard for examining the broader ethical considerations surrounding private societies. By fostering open dialogue, promoting ethical frameworks, and prioritizing transparency and accountability, we can strive to ensure that such societies contribute positively to a more just and compassionate world.
FAQs
- What are the potential benefits of joining a private society? Benefits can include networking opportunities, access to specialized knowledge or resources, and a sense of belonging. However, it’s crucial to weigh these benefits against potential ethical concerns.
- How can I ensure that a private society aligns with my values? Research the society thoroughly, paying attention to its mission statement, activities, and public perception. Consider speaking to current or former members to gain firsthand insights.
- What are some historical examples of private societies that have raised ethical concerns? History is replete with examples, some with more severe consequences than others. It’s crucial to learn from these examples and advocate for ethical conduct in all organizations.
Need Support?
For support and assistance regarding digital peace and related issues, please contact us:
- Phone: +44 20 4385 4663
- Email: [email protected]
- Address: Zone 34, Bac Giang, 260000, Vietnam
Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you.