Feudalism Developed As A Way For Medieval Societies To establish social order, administer justice, and organize military defense in the absence of strong centralized governments. This complex system, emerging after the fall of the Roman Empire, shaped the political, economic, and social landscape of Europe for centuries. It wasn’t a uniform system, varying regionally and evolving over time, but its core principles revolved around land ownership, loyalty, and service.
Understanding Why Feudalism Developed as a Way for Medieval Societies to Function
The collapse of the Roman Empire left a power vacuum. Centralized authority crumbled, leaving communities vulnerable to invasions and internal strife. In this context, feudalism offered a way to create local power structures, providing security and stability. Essentially, it was a system of mutual obligations: protection in exchange for service.
The Core Principles of Feudalism
At the heart of feudalism was the fief, a grant of land given by a lord to a vassal. In return for the fief, the vassal swore allegiance to the lord, promising military service and other forms of support. This created a hierarchical structure with the king at the top, followed by powerful nobles, then lesser lords, and finally, the peasants who worked the land.
- Land Ownership: Land was the foundation of wealth and power. Control over land meant control over resources and people.
- Loyalty and Service: Personal loyalty and oaths of fealty bound vassals to their lords. This created a network of reciprocal obligations.
- Decentralized Power: Feudalism distributed power among numerous lords, each ruling their own territory.
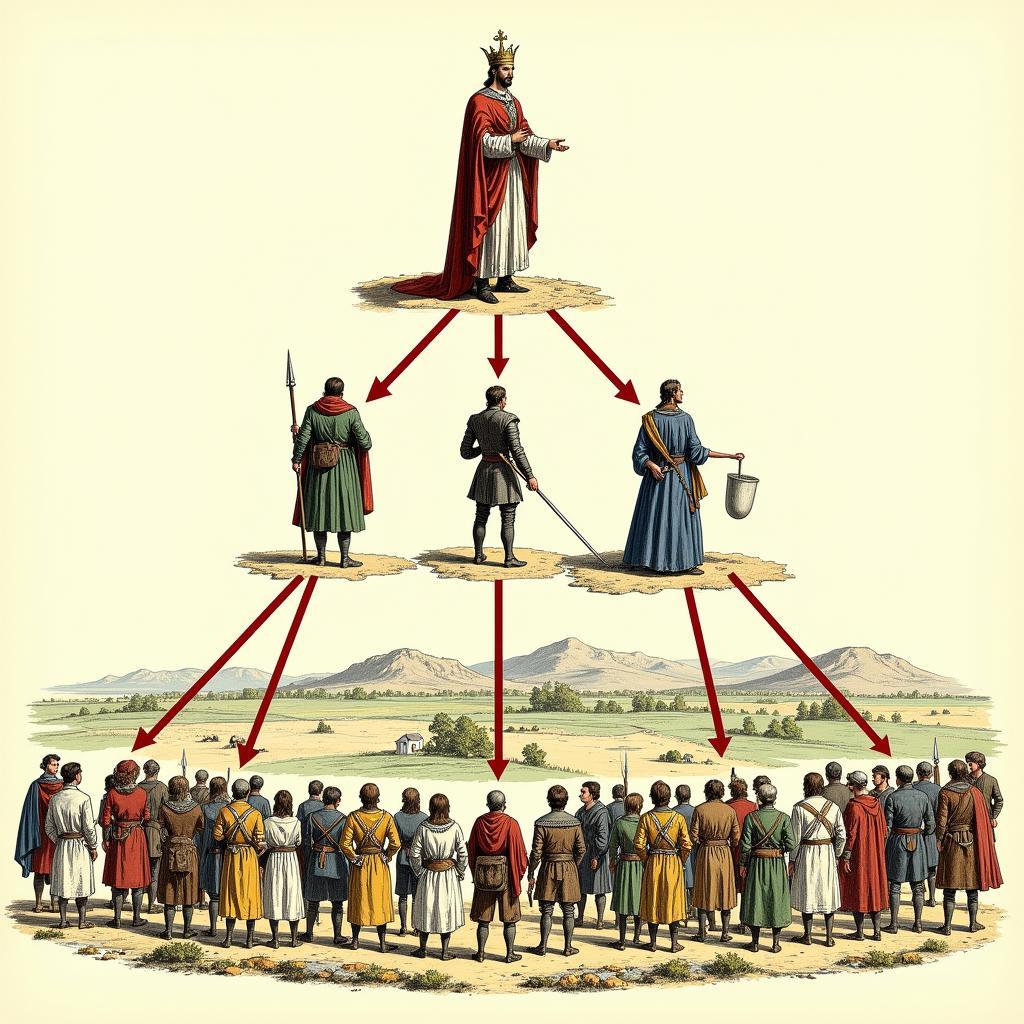 Medieval Feudal System Hierarchy Diagram
Medieval Feudal System Hierarchy Diagram
How Feudalism Shaped Medieval Life
Feudalism profoundly impacted every aspect of medieval society. It determined social status, economic activity, and even religious practices. The system enforced a rigid social hierarchy, with limited social mobility. Peasants, tied to the land, provided the agricultural labor that supported the entire system. Knights, trained warriors, provided military service to their lords. Nobles, holding vast estates, exercised considerable power within their territories.
Examining the Social and Economic Impact of Feudalism
The feudal system, while providing a degree of stability, also created significant inequalities. Peasants, despite being the backbone of the economy, had few rights and lived in poverty. The lord held considerable power over his vassals and peasants, controlling their lives and livelihoods. This power imbalance often led to exploitation and social unrest.
The Role of the Church in Feudal Society
The Church played a powerful role in feudal society. It owned vast tracts of land and held considerable political influence. The Church also provided education and social services, filling a gap left by the weakened central governments. It offered a sense of spiritual unity in a fragmented world.
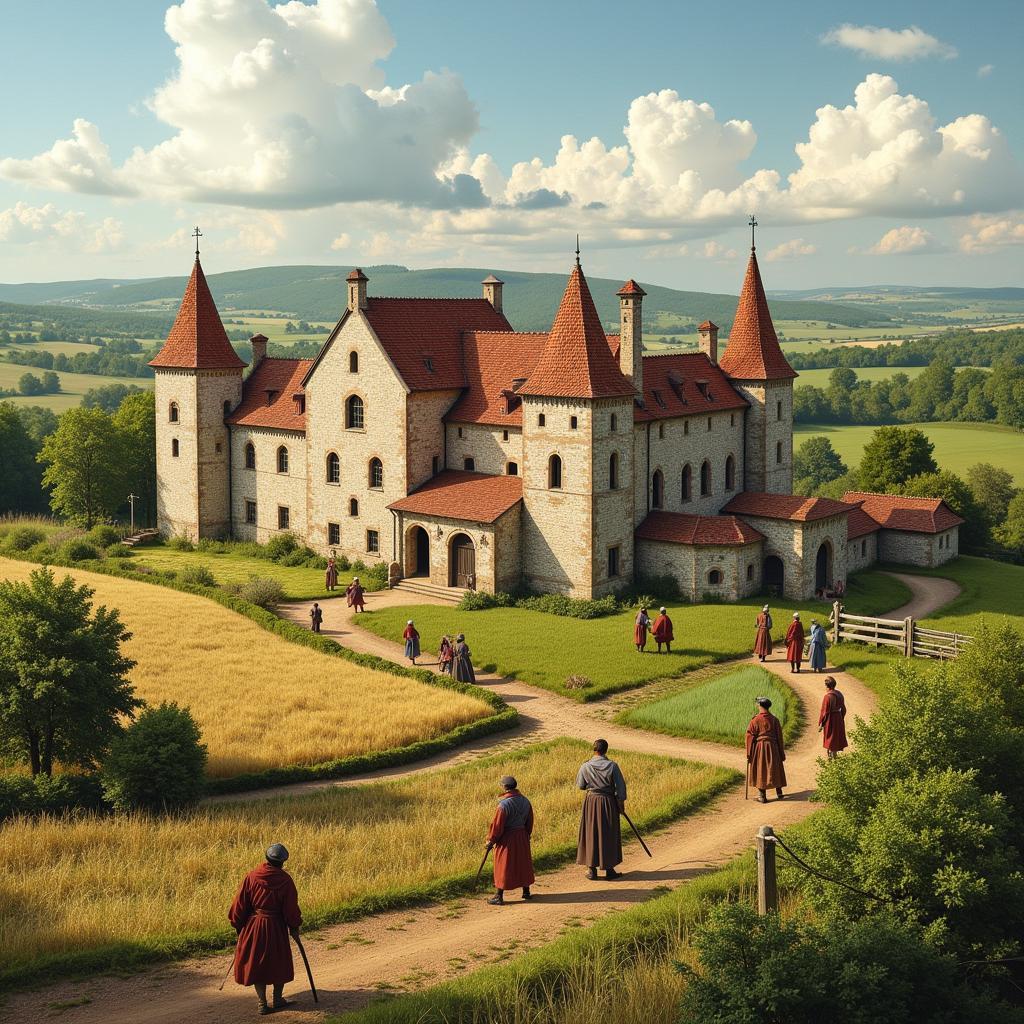 Medieval Manor and Agricultural Activities
Medieval Manor and Agricultural Activities
The Decline of Feudalism
Several factors contributed to the eventual decline of feudalism. The rise of towns and trade weakened the manorial system. The Black Death decimated the population, leading to labor shortages and social upheaval. The development of new military technologies, such as gunpowder, rendered feudal armies obsolete. The growth of centralized monarchies gradually consolidated power, challenging the decentralized authority of feudal lords.
“The strength of feudalism resided in its localized nature, but this also proved to be its weakness. As central authorities gained strength, the feudal system struggled to adapt.” – Dr. Eleanor Vance, Professor of Medieval History, University of Oxford (fictional).
Feudalism: A Legacy of Order and Inequality
Feudalism, while inherently unequal, provided a framework for order and stability in a turbulent era. It shaped the political and social landscapes of Europe, leaving a lasting legacy on legal systems, social structures, and cultural traditions. Understanding feudalism is crucial to understanding the development of Western civilization.
 Map of Feudal Europe Showing Land Divisions
Map of Feudal Europe Showing Land Divisions
Feudalism developed as a way for medieval societies to navigate a world without centralized authority. It provided security, albeit at a cost. While the system ultimately declined, its impact can still be felt today.
FAQ
- What was the main purpose of feudalism? To establish social order and provide security in the absence of strong central governments.
- Who was at the top of the feudal hierarchy? The king.
- What was a fief? A grant of land given by a lord to a vassal in exchange for service and loyalty.
- What factors led to the decline of feudalism? The rise of towns and trade, the Black Death, new military technologies, and the growth of centralized monarchies.
- What was the role of the Church in feudal society? It held significant land, political influence, and provided education and social services.
- How did feudalism impact medieval life? It determined social status, economic activity, and religious practices.
- Was feudalism a fair system? No, it created significant social and economic inequalities.
Situations where feudalism is discussed
- History classes examining medieval Europe
- Discussions about social hierarchy and inequality
- Analyses of political and economic systems
Further Reading
- The Rise and Fall of Feudalism
- The Impact of the Church on Medieval Society
Contact us for support: Phone: 02043854663, Email: [email protected], Address: Khu 34, Bắc Giang, 260000, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer service team.