Society Faces A Short-run Tradeoff Between Inflation And Unemployment. This complex relationship, often referred to as the Phillips Curve, suggests that efforts to reduce unemployment can lead to increased inflation, while attempts to curb inflation can result in higher unemployment. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for policymakers and citizens alike.
The Phillips Curve: A Balancing Act
The Phillips Curve illustrates the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment. When unemployment is low, businesses compete for a limited pool of workers, driving up wages. These increased labor costs are often passed on to consumers as higher prices, leading to inflation. Conversely, when unemployment is high, there’s less pressure on wages and prices, resulting in lower inflation.
This tradeoff presents a significant challenge for governments. Do they prioritize stable prices, even if it means higher unemployment? Or do they focus on job creation, accepting the risk of rising inflation? The answer is rarely straightforward and depends on a variety of economic and political factors.
One key factor is the expected rate of inflation. If people expect prices to rise, they may demand higher wages, which can further fuel inflation, creating a self-fulfilling prophecy. Managing these expectations is crucial for policymakers.
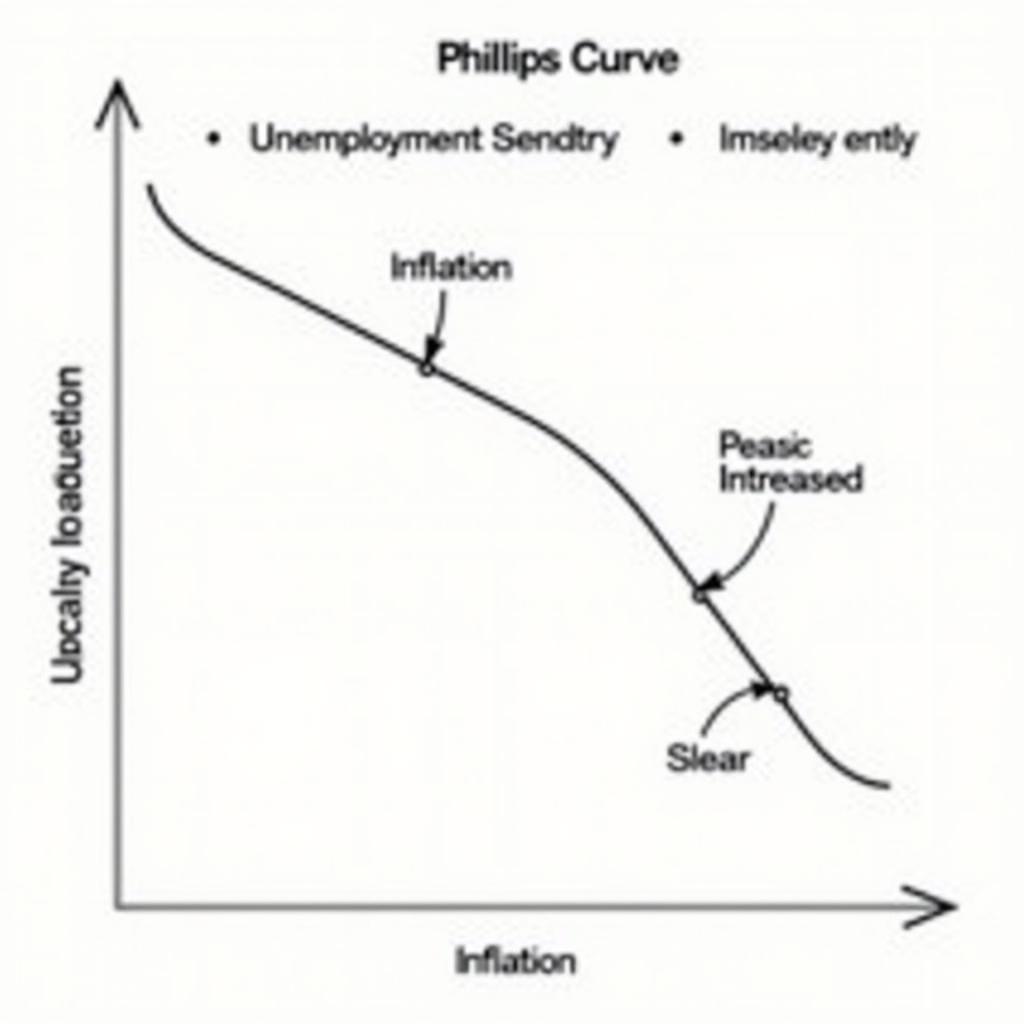 Phillips Curve Showing the Relationship between Inflation and Unemployment
Phillips Curve Showing the Relationship between Inflation and Unemployment
Navigating the Tradeoff: Policy Implications
Policymakers use various tools to navigate the inflation-unemployment tradeoff. Fiscal policy, which involves government spending and taxation, can influence aggregate demand and impact both inflation and unemployment. Monetary policy, controlled by central banks, primarily focuses on managing interest rates and the money supply to achieve price stability and full employment.
For example, during an economic downturn with high unemployment, a central bank might lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and investment, stimulating economic activity and creating jobs. However, this can also increase the risk of inflation. Finding the right balance is crucial. The specific policies implemented depend on the unique circumstances of each economy.
 Monetary and Fiscal Policy Tools Balancing Inflation and Unemployment
Monetary and Fiscal Policy Tools Balancing Inflation and Unemployment
What Causes the Short-Run Tradeoff?
The short-run tradeoff exists because wages and prices do not adjust instantaneously. In the short run, an unexpected increase in demand can lead to higher production and employment, but also higher prices, as businesses struggle to meet the increased demand with existing resources. Over time, however, wages and prices adjust, and the economy moves towards a new equilibrium.
Dr. Amelia Hernandez, a renowned economist at the University of California, Berkeley, emphasizes the importance of understanding this dynamic: “The short-run tradeoff is a crucial concept in macroeconomics. Recognizing its existence allows policymakers to make informed decisions about how to manage the economy and strive for sustainable growth.”
Long-Run Implications: Sustainable Growth
While society faces a short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment, the long-run relationship is less clear. Some economists argue that there is no long-run tradeoff, meaning that attempts to keep unemployment artificially low will only result in higher inflation without any lasting benefit for employment. Instead, they advocate for policies that promote sustainable economic growth, which can lead to both lower unemployment and stable prices in the long run.
Professor David Chen, an expert in labor economics at the London School of Economics, adds, “Focusing on long-term sustainable growth is essential for achieving both price stability and full employment. This requires investments in education, infrastructure, and technological innovation.”
 Sustainable Economic Growth Leading to Long-Term Stability
Sustainable Economic Growth Leading to Long-Term Stability
Conclusion
Society faces a short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment. This complex relationship requires careful management by policymakers. Understanding the dynamics of the Phillips Curve and implementing appropriate fiscal and monetary policies is essential for achieving both price stability and full employment. Ultimately, the goal is to promote sustainable economic growth that benefits all members of society.
FAQs
- What is the Phillips Curve?
- How does the Phillips Curve relate to inflation and unemployment?
- What are the policy implications of the Phillips Curve?
- Is there a long-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment?
- How can sustainable economic growth be achieved?
Need Help? Contact Us!
For further assistance and information, please don’t hesitate to contact us:
Phone: 02043854663
Email: [email protected]
Address: Khu 34, Bac Giang, 260000, Vietnam
Our customer support team is available 24/7 to answer your questions and provide support. We also encourage you to explore other articles on our website related to economics, peacebuilding, and social justice. We believe that by working together, we can create a more peaceful and prosperous world for all.