Emile Durkheim’s theories offer a profound understanding of modern society, exploring the complexities of social solidarity, the division of labor, and the impact of rapid social change. His work remains remarkably relevant in today’s world, helping us navigate the challenges and opportunities of an increasingly interconnected global society. emile durkheim viewed society as
Understanding Durkheim’s View of Modern Society
Durkheim, a founding figure of sociology, argued that modern societies were characterized by a shift from mechanical solidarity, found in traditional communities, to organic solidarity. This transition, driven by the increasing division of labor, led to greater interdependence among individuals. In simpler societies, shared beliefs and values bound people together. Modern society, however, relies on the specialization of roles and functions, creating a web of interconnectedness.
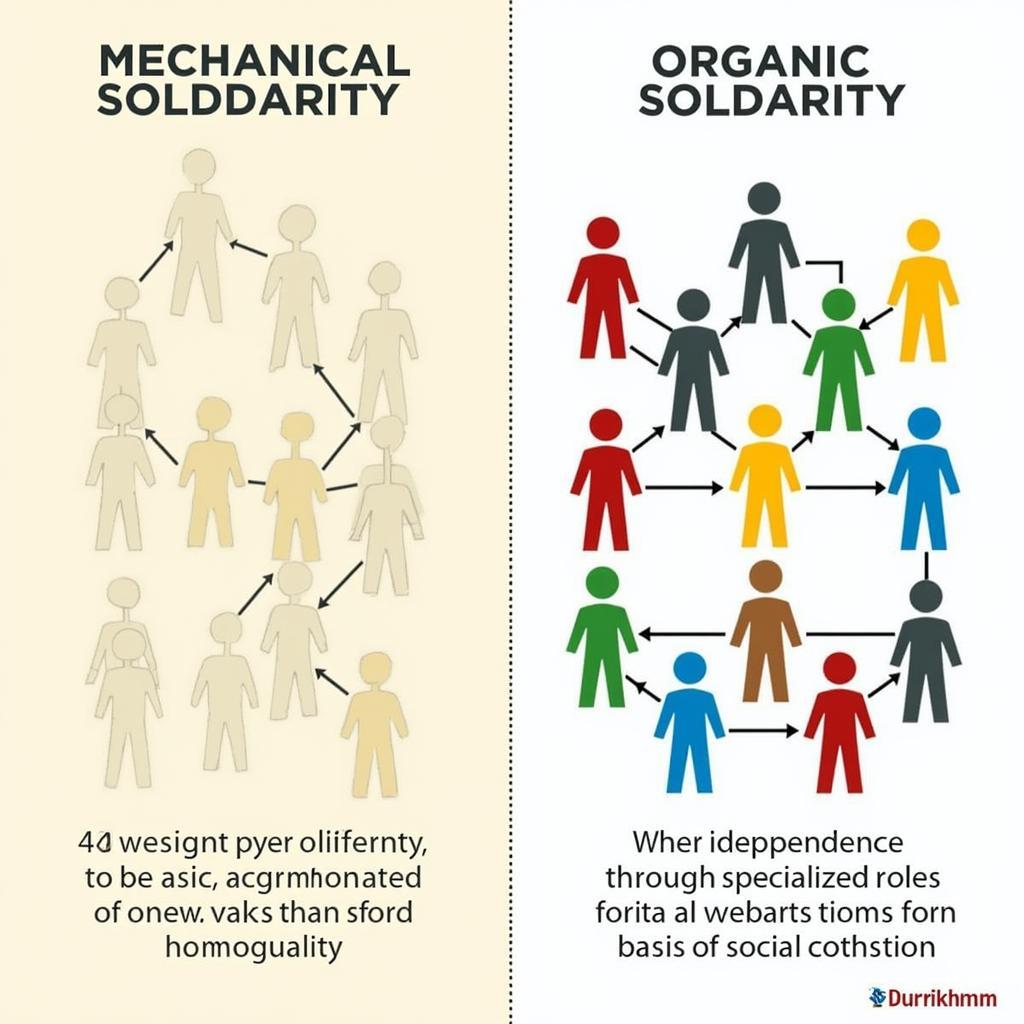 Durkheim's Mechanical and Organic Solidarity
Durkheim's Mechanical and Organic Solidarity
Durkheim recognized that this shift wasn’t without its problems. He coined the term “anomie” to describe the feeling of normlessness and disconnection that can arise in modern society. Rapid social change, he argued, could erode traditional values and leave individuals feeling lost and alienated. This anomie, in turn, could lead to social unrest and even deviance.
The Division of Labor and its Social Implications
Central to Durkheim’s analysis of Emile Durkheim Modern Society is the concept of the division of labor. He saw it as more than just an economic principle; it was a fundamental aspect of social organization. The specialized roles in modern society, while creating interdependence, could also lead to fragmentation and inequality. why is marriage important to society
How does the division of labor affect social cohesion?
Durkheim argued that the division of labor, while potentially divisive, could also be a source of social cohesion. He believed that through specialized roles, individuals become reliant on one another, fostering a sense of collective consciousness. This interconnectedness, however, requires careful management to prevent excessive individualism and anomie.
Emile Durkheim’s Relevance Today
Durkheim’s work continues to resonate in the 21st century. Globalization, technological advancements, and rapid social change have intensified many of the issues he identified, such as anomie and social fragmentation. anthropology examines spirituality and religion in terms of the societys Understanding his theories can provide valuable insights into contemporary social problems and help us build a more just and cohesive society.
What can we learn from Durkheim in a globalized world?
Durkheim’s focus on social solidarity reminds us of the importance of building strong social bonds in an increasingly interconnected world. His insights into the division of labor can help us address the challenges of inequality and social fragmentation that often accompany globalization. society the basics
Conclusion
Emile Durkheim’s work on emile durkheim modern society provides a crucial framework for understanding the social forces shaping our world. His insights into social solidarity, the division of labor, and the challenges of rapid social change remain remarkably relevant today, offering valuable guidance for navigating the complexities of a globalized world and building a more just and peaceful future.
FAQ
- What is mechanical solidarity according to Durkheim?
- How does organic solidarity differ from mechanical solidarity?
- What is anomie and why is it relevant to modern society?
- How does the division of labor contribute to both social cohesion and fragmentation?
- What are some of the key challenges facing modern societies according to Durkheim’s perspective?
Further Exploration
- Explore the concept of collective consciousness in more detail.
- Investigate the impact of social media on social solidarity.
- Examine the relationship between anomie and social deviance.
- what is an industrialized society
Need Support?
Contact us 24/7:
Phone: 02043854663
Email: [email protected]
Address: Khu 34, Bac Giang, 260000, Vietnam.