Organic society is a concept that describes a social system with inherent interconnectedness and interdependence, much like a living organism. It emphasizes the natural evolution of social structures, roles, and norms, often contrasting with planned or artificially constructed societies. This concept has deep roots in sociological thought and offers valuable insights into how societies function and evolve.
Understanding what constitutes an organic society requires exploring its core principles, historical context, and contrasting perspectives. This model often highlights the importance of tradition, shared values, and gradual change. It suggests that social order arises naturally from the interactions of individuals and groups, rather than being imposed from above.
Defining the Characteristics of an Organic Society
Several key characteristics define an organic society. These include a strong sense of community, shared values and beliefs, and a clear division of labor based on natural aptitudes and social roles. This model often emphasizes the importance of family, kinship, and local communities as foundational building blocks of the social structure. It also suggests that individuals find meaning and purpose through their contribution to the larger social whole.
A key thinker associated with the concept of organic society is functionalist Émile Durkheim, who viewed society as an integrated whole with interconnected parts. His work emphasized the importance of social solidarity and the role of shared values and beliefs in maintaining social order. functionalist émile durkheim viewed society as: He believed that societies evolve naturally through a process of differentiation and integration, where specialized institutions develop to perform specific functions.
Differentiation in this context refers to the increasing complexity and specialization of social roles and institutions. Integration, on the other hand, refers to the processes that bind these differentiated parts together into a cohesive whole.
How does an Organic Society Contrast with a Mechanistic One?
The concept of organic society is often contrasted with that of a mechanistic society. A mechanistic society is characterized by formalized structures, hierarchical relationships, and a focus on efficiency and productivity. In such societies, social order is maintained through rules, regulations, and external controls, rather than through shared values and internalized norms. Think of a large corporation with its clearly defined roles, hierarchical structure, and focus on maximizing profit as a prime example of a mechanistic system. 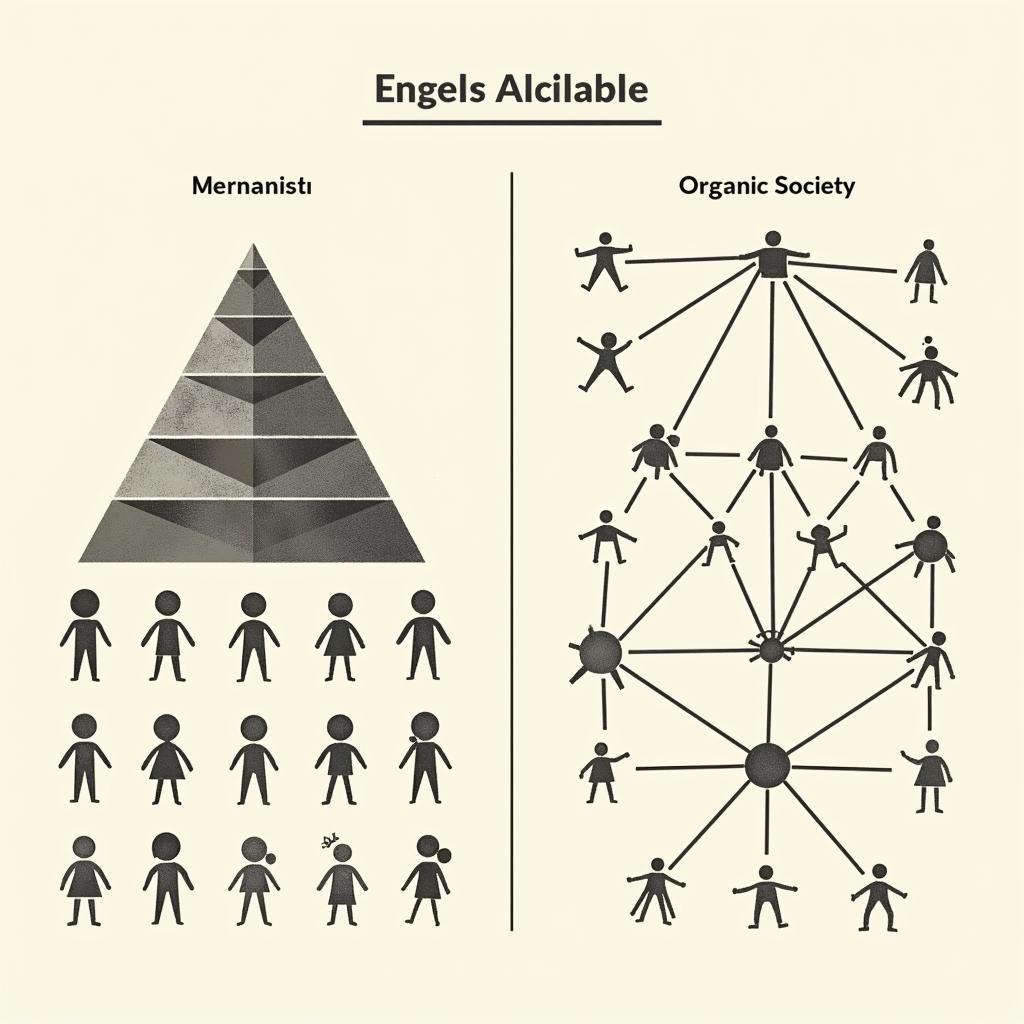 Mechanistic vs. Organic Society Structure
Mechanistic vs. Organic Society Structure
In contrast, an organic society prioritizes cooperation, community, and the overall well-being of its members. While mechanistic societies may be more efficient in achieving specific goals, organic societies are often seen as more resilient and adaptable to change due to their decentralized nature and emphasis on community support.
The Role of Tradition and Shared Values in an Organic Society
Tradition and shared values play a crucial role in maintaining social cohesion and stability within an organic society. They provide a framework for understanding the world, making decisions, and interacting with others. These shared values are often passed down through generations and serve as a source of identity and belonging for individuals within the community.
While an organic society embraces tradition, it doesn’t necessarily reject change altogether. Change is viewed as a natural and gradual process, occurring through adaptation and evolution rather than through radical upheaval. This organic approach to change allows for the preservation of core values while also accommodating new ideas and practices that enhance the overall well-being of the community.
american chemical society organic chemistry study guide provide in-depth explanations of organic compounds, their reactions, and their role in shaping our world. Understanding the building blocks of organic matter, from a scientific perspective, can provide insights into the complex interplay of elements within a natural system, much like how individuals and groups interact within an organic society.
What are some examples of Organic Societies?
Many indigenous cultures around the world exhibit characteristics of organic societies. These communities often prioritize communal living, shared resources, and a deep connection to the natural environment. Their social structures are typically based on kinship ties and traditional customs, emphasizing cooperation and mutual support.  Examples of Organic Societies
Examples of Organic Societies
Conclusion: Understanding Organic Society in a Modern Context
While the concept of organic society may seem idealized in our increasingly complex and interconnected world, it still offers valuable insights into how we can foster stronger communities and promote social harmony. Understanding the principles of organic society can help us to appreciate the importance of social cohesion, shared values, and the interconnectedness of all things. american chemical society organic chemistry exam practice can help students better understand the intricacies of organic chemistry. Similarly, exploring the concept of organic society can provide valuable insights into the complexities of human social structures. By embracing the principles of cooperation, community, and mutual support, we can strive to create a more peaceful and harmonious world.
american chemical society organic chemistry exam pdf
FAQ:
- What is the core difference between organic and mechanistic societies?
- How do shared values contribute to an organic society?
- Can modern societies still exhibit characteristics of organic societies?
- What is the role of tradition in an organic society?
- How does Émile Durkheim’s work relate to the concept of organic society?
- What are some real-world examples of organic societies?
- How can understanding organic societies contribute to building a more peaceful world?
Need further information? Explore these related articles on our website: “The Importance of Community in Building a Peaceful Society” and “The Role of Tradition in Modern Society.”
When you need support, contact us by Phone: 02043854663, Email: [email protected], or visit us at Zone 34, Bac Giang, 260000, Vietnam. We have a 24/7 customer support team.